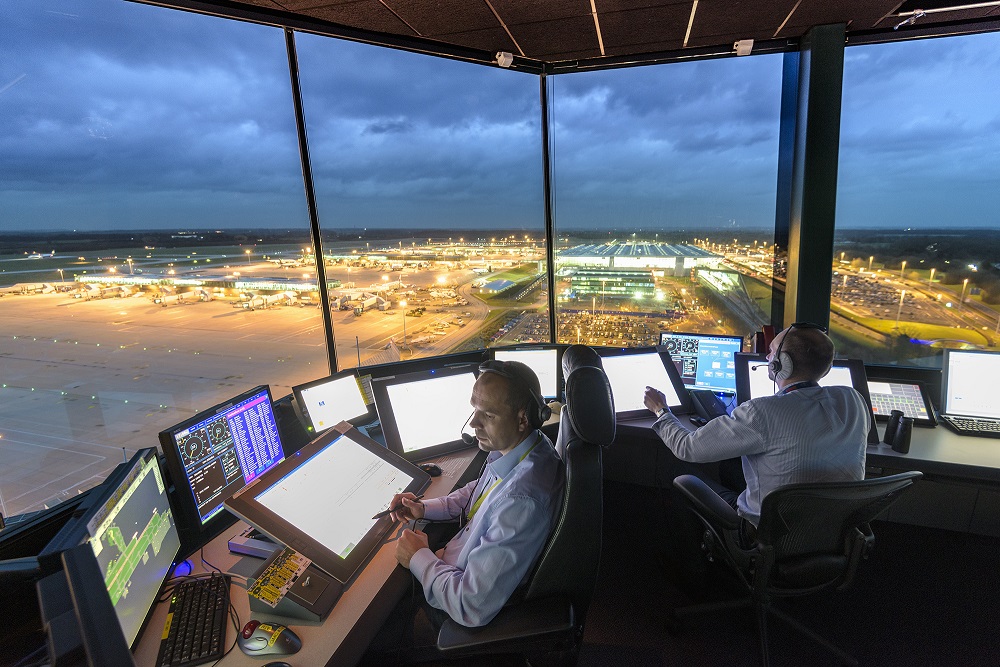
Air Traffic Control (ATC) is a critical aspect of the aviation enterprise, ensuring the secure and green movement of aircraft in the sky and on the ground. ATC services are provided by incredibly educated professionals who paint from control towers, radar centers, and en-path centers to manipulate air traffic and preserve separation among planes.
These controllers speak with pilots, offer clearances for takeoff and landing, and monitor airspace for ability conflicts or dangers. By coordinating with pilots, airlines, airports, and aviation authorities, Air Traffic Control plays a critical role in making sure the safety of air tours and minimizing delays. With the ongoing evolution of era and the implementation of modern answers, the future of Air Traffic Control promises to be even safer, greater efficient, and more sustainable.
Introduction

Importance of Air Traffic Control in Aviation
Picture this: Without Air Traffic Control, the skies would resemble a chaotic loose-for-all, akin to rush hour visitors with no traffic lighting or avenue signs and symptoms. It’s ATC that keeps our airways secure and ensures that planes can navigate the giant expanse of the sky without colliding.
- Think of Air Traffic Control because the dad or mum angels of aviation, tirelessly running behind the scenes to save you mid-air collisions, keep order in the skies, and facilitate the easy go with the flow of air site visitors.
- From the moment a plane takes to the air to the moment it touches down, Air Traffic Control is there, orchestrating each flow, guiding pilots through the skies, and ensuring that each flight reaches its destination correctly and on time.
Overview of What Air Traffic Control Entails
So, what exactly does Air Traffic Control entail? Well, it is extra than only a tower on the airport or a bunch of radar screens. Air Traffic Control is a complex system comprising numerous factors, all working in harmony to ensure the safety and performance of air tours.
- At its center, Air Traffic Control includes the coordination and supervision of plane movements, each at the floor and within the air. It’s about managing the go with the flow of visitors, presenting pilots with critical records and instructions, and resolving conflicts to save you injuries.
- But it is now not just about giving orders and directing traffic. Air Traffic Control additionally includes tracking climate conditions, communicating with pilots and different Air Traffic Control facilities, and staying alert to any capability threats or emergencies.
Purpose of the Blog Post
Now, you are probably questioning, why must I trouble getting to know approximately Air Traffic Control? Well, whether you’re a seasoned aviation fanatic or just a person who is curious about how planes live safely in the sky, expertise in the basics of ATC can give you a whole new appreciation for the magic of flight.
- By dropping mild at the inner workings of Air Traffic Control, this weblog publishes goals to demystify a subject it’s frequently shrouded in thriller. We’ll spoil down the important ideas, discover the position of ATC in aviation, and perhaps even encourage you to remember a profession in this dynamic subject.
- So buckle up, expensive reader, and get equipped to soar to new heights as we dive into the charming international of Air Traffic Control. Whether you’re a common flyer, an aviation enthusiast, or just someone who is curious about how planes navigate the skies, there’s something here for everybody. Let’s embark on this journey together and elevate our expertise in Air Traffic Control!
What is Air Traffic Control?
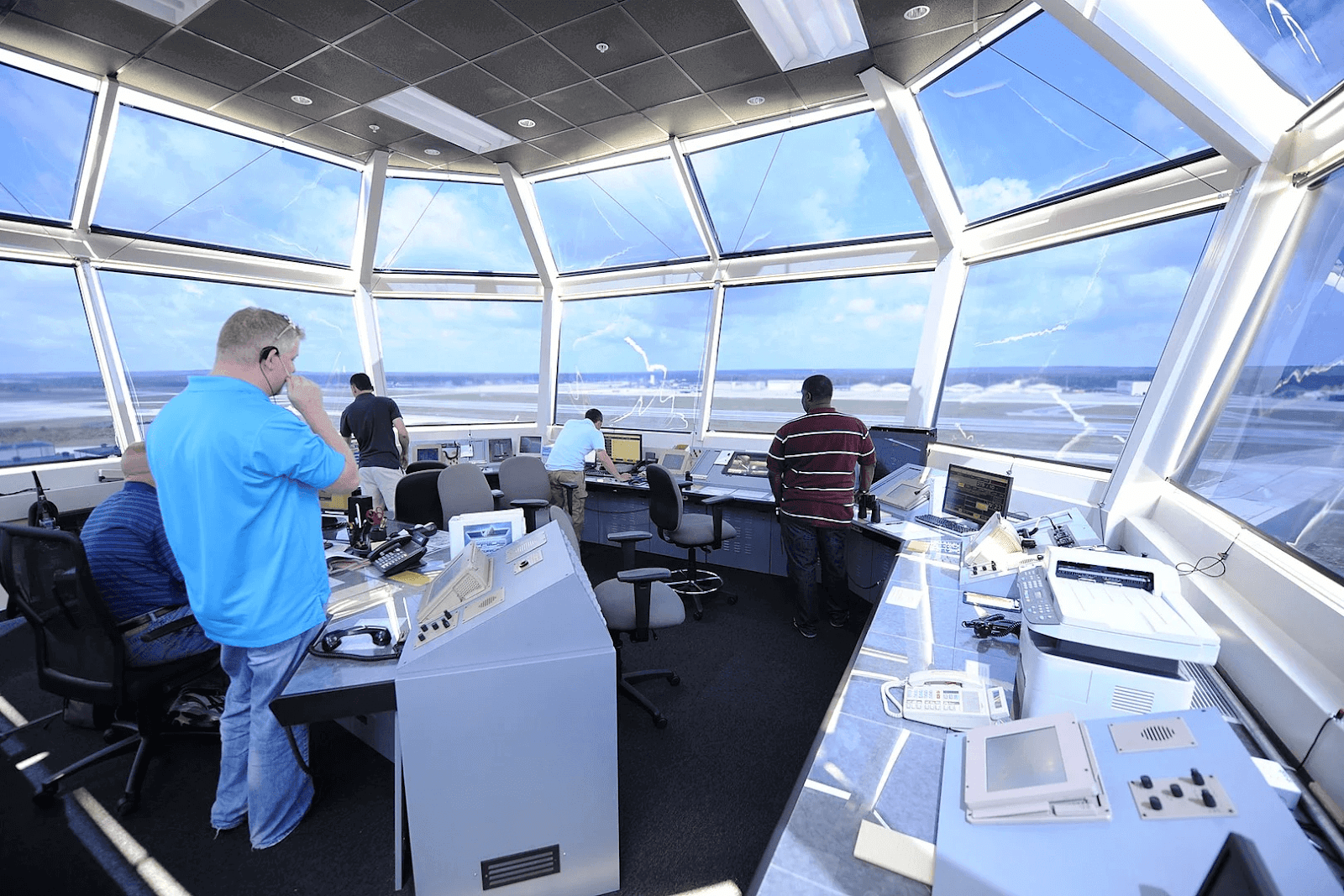
Definition and Scope
Air Traffic Control, or ATC for brief, is much like the conductor of a symphony, orchestrating the movements of aircraft to make sure they navigate the skies very well and efficiently. It’s the backbone of aviation, encompassing an extensive variety of obligations and duties that preserve our skies stable for excursion. ATC is not just about guiding planes inside and out of airports; it’s approximately handling the entire airspace, from takeoff to landing.
- Definition: Air Traffic Control is the technique of directing and tracking plane movements, every at the floor and inside the air, to save you from collisions and ensure the secure and orderly float of air visitors.
- Scope: ATC covers the whole thing from supplying pilots with clearance for takeoff and landing to guiding them via congested airspace, tracking weather conditions, and coordinating with other ATC facilities.
Historical Background
The roots of Air Traffic Control can be traced again to the early days of aviation whilst the skies were a wild, unregulated frontier. In the early 20th century, as aviation generation superior and extra planes took to the skies, the want for a few forms of management have ended up increasingly apparent. The first rudimentary styles of ATC emerged within the 1920s, generally targeted on coping with air website visitors round airports and essential cities.
- Early Days: The first air visitors to manipulate the tower became hooked up in Cleveland, Ohio, in 1930, marking the start of the current ATC.
- World War II: The demands of wartime aviation introduced approximately enormous improvements in ATC technology and procedures, laying the idea for the modern-day air website traffic management device.
- Post-War Era: With the fast growth of business aviation within the put up-struggle generation, the want for a greater whole and complicated ATC
Evolution of Air Traffic Control Systems
Since its humble beginnings, Air Traffic Control has gone through a super evolution, pushed via advances in technology, adjustments in air excursion patterns, and the ever-present need to decorate protection and performance. From simple radio communique and visual remarks to sophisticated radar systems and computerized automation, ATC has come an extended manner as a substitute quick period.
- Radar Revolution: The advent of radar technology inside the mid-twentieth century revolutionized ATC, allowing controllers to single plane greater accurately and successfully.
- Automation and Digitalization: The creation of computers and the digital era in the latter half of the 20 th century paved the way for automation in ATC, streamlining operations and enhancing protection.
- Next Gen Air Traffic Management: Today, the focus is on Next Generation Air Traffic Management systems, which leverage superior technologies together with satellite navigation, data communications, and synthetic intelligence to further improve protection, ability, and efficiency.
Air Traffic Control is the invisible hand that publishes the skies, ensuring that thousands and thousands of passengers reach their locations adequately and on time. From its humble beginnings to its cutting-edge contemporary systems, ATC has come an extended manner, evolving to satisfy the ever-growing demands of modern-day aviation. So the subsequent time you appear up at the sky and notice planes crisscrossing overhead, take a moment to comprehend the important position of Air Traffic Control in retaining our skies secure and our flights clean.
The Role of Air Traffic Controllers
Responsibilities and Duties
Ever confused who is behind the scenes making sure that planes navigate the skies thoroughly? That’s wherein Air Traffic Controllers (ATCs) are to be had in. These unsung heroes have an important position in aviation, with various duties and responsibilities that hold our skies stable and our flights on target.
- Guiding Aircraft: ATCs are liable for supplying clearances for takeoff and touchdown, in addition to guiding planes via certain flight paths and airspace.
- Traffic Management: They display and manage the go with the flow of air website traffic, ensuring that planes keep stable distances and avoid collisions.
- Communication: ATCs preserve everyday communique with pilots, imparting them with important data, commands, and updates all through their journey.
Qualifications and Training
It takes courage to become an air traffic controller. To handle the extreme stress of an ATC tower, one needs a completely different set of skills, knowledge, and training. Here’s what it takes to sign up in the ranks of those aviation specialists:
- Education: While specific educational necessities vary with the aid of u . S ., maximum ATCs need as a minimum an excessive faculty degree or equivalent.
- Training: ATCs go through rigorous training programs that cover topics at the side of aviation policies, airspace manipulation, radar operation, and verbal exchange protocols.
- Certification: Upon finishing their training, ATCs should reap certification from the relevant aviation authority, demonstrating their competence to govern air website online traffic properly and efficiently.
Stress Factors and Challenges
Working as an Air Traffic Controller may be enormously worthwhile, however it’s also one of the most stressful jobs within the international community. The high-stakes nature of the job, coupled with the steady pressure to make cut-up-second decisions, can take a toll on even the most seasoned professionals. Here are some of the pressure factors and demanding situations that ATCs face:
- High Workload: ATCs frequently juggle more than one aircraft simultaneously, specially throughout peak visitors intervals, mainly to excessive degrees of intellectual and bodily fatigue.
- Critical Decision Making: ATCs are responsible for making vital selections in actual-time, along with rerouting aircraft to avoid horrific weather or resolving conflicts between planes.
- Emergency Situations: Handling emergencies, which includes engine disasters or clinical emergencies onboard a plane, requires brief thinking and calm beneath strain.
Components of Air Traffic Control Systems
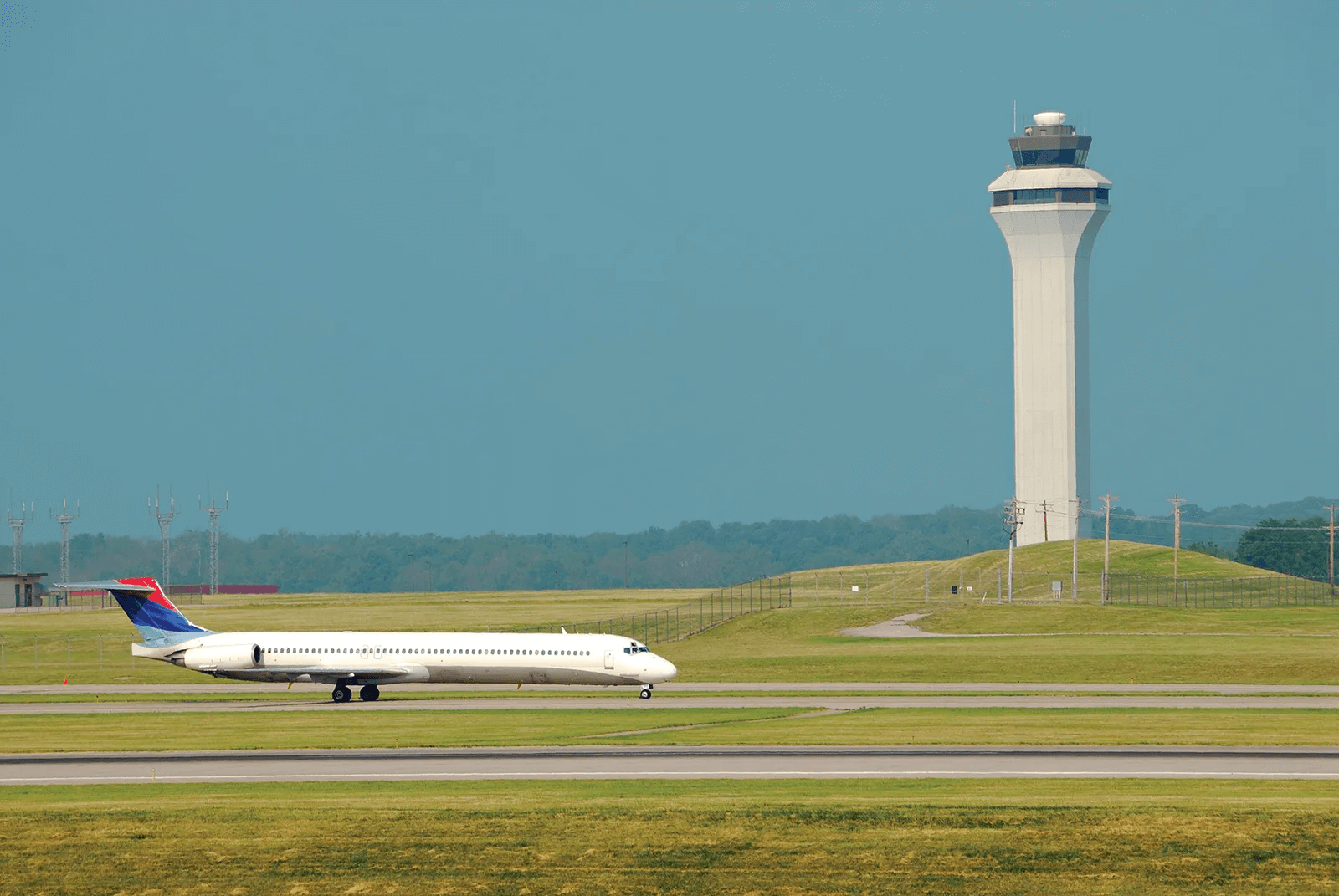

Radar Systems
When it involves maintaining music of planes in the sky, radar systems are the eyes and ears of Air Traffic Control. These sophisticated technologies use radio waves to stumble on and tune the location, speed, and altitude of the plane, permitting controllers to display their actions in actual-time.
- Primary Radar: Traditional radar systems soar radio waves off plane to determine their place and trajectory.
- Secondary Radar: In addition to number one radar, secondary radar systems rely on transponders onboard planes to provide extra information, along with aircraft identity and altitude.
- Surveillance Radar: Modern radar structures incorporate advanced surveillance technology, such as Mode S and ADS-B, which provide improved accuracy and coverage.
Communication Equipment
Clear and reliable verbal exchange is critical for steady and efficient air traffic manipulation. Air Traffic Controllers rely on some conversation devices to live in contact with pilots and different ATC facilities, making sure that vital facts are exchanged quickly and correctly.
- VHF Radios: Very High Frequency (VHF) radios are the primary method of verbal exchange between ATC and aircraft. They feature specific frequencies allocated for aviation use.
- Data Links: Digital communique systems, consisting of CPDLC (Controller-Pilot Data Link Communications) and ACARS (Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System), permit for the exchange of textual content-based total messages among controllers and pilots.
- Emergency Communication: Dedicated emergency frequencies and protocols make sure that controllers can talk efficiently with planes in misery or emergency situations.
Navigation Aids
Navigating through the skies requires specific navigation aids to manual planes thoroughly to their locations. Air Traffic Control is based on a network of floor-based and satellite tv for pc-based total navigation systems to offer correct positioning facts to pilots and controllers alike.
- VOR/DME: Very High Frequency Omani-directional Range (VOR) and Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) provide pilots with dependable navigation steering primarily based on radio indicators transmitted from floor stations.
- GPS: The Global Positioning System (GPS) revolutionized air navigation through imparting correct positioning records the usage of satellite signals. GPS is now broadly used for en-course navigation and precision tactics.
- ILS: During approach and touchdown, aircraft can receive accurate guidance from the Instrument Landing System (ILS), a ground-based navigational aid that is especially helpful in low-visibility conditions.
Automation and Technology
In the virtual age, automation and generation play an increasingly more extensive position in Air Traffic Control. Advanced software program systems and automation tools help streamline operations, decorate protection, and improve performance in dealing with air traffic.
- ATC Automation: Automated systems, together with radar information processing and warfare detection gear, help controllers in handling airspace and figuring out capacity conflicts.
- NextGen Technologies: Next Generation Air Traffic Management systems leverage modern technology, along with synthetic intelligence and machine getting to know, to optimize airspace utilization, reduce delays, and decrease environmental impact.
- Remote Towers: Remote tower generation permits for the far flung operation of air site visitors to manipulate towers, enabling controllers to manage multiple airports from a centralized place.
Airspace Classification and Regulation

Types of Airspace
Ever wondered why the sky isn’t always just one large open space for planes to roam freely? Well, it really is due to the fact airspace is in reality divided into unique classes, each with its personal set of guidelines and regulations. Understanding these classifications is crucial for pilots and Air Traffic Controllers alike to make certain safe and orderly air travel.
- Controlled Airspace: This is airspace wherein ATC has authority and obligation for controlling air visitors. It consists of airspace around airports and along airways, wherein aircraft should adhere to particular clearance requirements.
- Uncontrolled Airspace: In comparison, out of control airspace is not actively monitored or controlled by ATC. However, pilots are nonetheless required to stick to certain regulations and techniques to keep separation from other aircraft.
- Special-Use Airspace: Special-use airspace is exact for unique functions, which includes army operations, aerial refueling, or checking out of planes. Pilots should gain clearance before entering those regions.
Air Traffic Control Zones
Within controlled airspace, there are different zones that serve precise functions and require special ranges of clearance from ATC. These zones help manage air site visitors more correctly and ensure the safety of all aircraft working within them.
- Terminal Control Area (TCA): Also known as the Terminal Control Zone (TCZ), that is the airspace surrounding principal airports in which ATC provides method and departure control services.
- Control Area (CTA): Control areas are large segments of controlled airspace that enlarge past TCAs and cowl en-path visitors. ATC en-course manipulate offerings inside CTAs to make certain secure separation of aircraft.
- Control Zone (CTR): Control zones are mounted round smaller airports to manipulate offerings for arriving and departing aircraft. Pilots ought to obtain clearance from ATC before entering or operating within a CTR.
Regulations and Compliance
To hold the skies safe and orderly, airspace policies are enforced through aviation governments round the sector. These rules govern the whole lot from minimum secure altitudes to airspace regulations and pilot qualifications. Compliance with these guidelines is critical for all pilots and Air Traffic Controllers to hold the integrity of the air visitors management gadget.
- Minimum Safe Altitudes: Pilots must adhere to minimum safe altitudes when flying over extraordinary sorts of terrain, consisting of populated regions, congested regions, and open water.
- Airspace Restrictions: Certain areas of airspace may be limited or prohibited because of protection worries, navy operations, or different reasons. Pilots must be privy to those restrictions and gain important clearances earlier than getting into constrained airspace.
- Pilot Qualifications: Pilots should keep valid licenses and ratings issued by means of the relevant aviation authority to operate inside controlled airspace. Additionally, they need to go through ordinary schooling and talent assessments to ensure compliance with policies.
Air Traffic Control Procedures

Ground Control
Ever puzzled how planes navigate the labyrinth of taxiways and runways at airports? That’s in which Ground Control is available. This department of Air Traffic Control is answerable for handling aircraft actions on the ground, ensuring safe and efficient taxiing to and from the runway.
- Taxi Clearance: Ground Control gives pilots clearance to taxi to and from their targeted gates, in addition to commands on which taxiways to use.
- Gate Assignments: They additionally coordinate gate assignments for arriving aircraft, ensuring that gates are to be had and ready for incoming flights.
- Runway Clearance: Ground Control authorizes aircraft to move active runways, coordinating with Tower Control to ensure secure separation from departing and arriving planes.
Tower Control
Once a plane is ready to take off or land, it enters the area of Tower Control. Tower controllers paintings from the enduring manage towers at airports, overseeing all runway operations and making sure the secure and orderly drift of air traffic.
- Takeoff Clearance: Tower Control presents clearance for aircraft to take off, coordinating with Ground Control to make certain that the runway is clear and secure for departure.
- Landing Clearance: They additionally clear the plane for touchdown, offering sequencing and spacing commands to preserve safe separation among arriving flights.
- Visual Observations: Tower controllers rely upon visual observations and radar data to monitor aircraft moves on and around the runway, intervening to prevent conflicts and make certain safety.
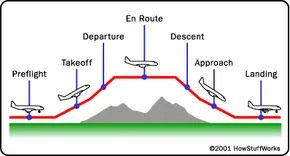
En-route Control
Once airborne, aircraft input the world of En-path Control. These controllers are accountable for managing air site visitors in specific airspace sectors, guiding aircraft through their planned routes and ensuring secure separation from different site visitors.
- Route Clearances: En-path controllers offer pilots with route clearances, directing them alongside installed airlines or direct routes to their destinations.
- Altitude Assignments: They additionally assign altitudes to aircraft to keep safe vertical separation and prevent mid-air collisions.
- Weather Monitoring: En-path controllers reveal climate conditions alongside flight routes and offer pilots with updates and advisories to assist them navigate appropriately via changing climate styles.
Approach and Departure Control
As planes method their vacation spot airports or go away from them, they come under the jurisdiction of Approach and Departure Control. These controllers manipulate the transition of the plane between en-route airspace and the terminal place.
- Arrival Sequencing: Approach controllers sequence arriving planes for landing, providing spacing commands to ensure safe separation on final approach.
- Departure Clearance: Departure controllers clear aircraft for takeoff, coordinating with Tower Control to ensure a smooth departure and secure integration into en-route visitors.
- Radar Vectoring: Approach controllers may additionally use radar vectoring to manual plane to the final approach course or to navigate round climate or visitors, offering particular headings to maintain separation.
Collaboration with Other Aviation Entities

Coordination with Pilots
Ever wondered how Air Traffic Control and pilots work together to make sure secure and efficient flights? Well, it’s all approximately collaboration. ATC and pilots communicate intently during each flight, replacing critical information and operating together to navigate the complexities of the skies.
- Clearances and Instructions: ATC provides pilots with clearances for takeoff, landing, and changes to their flight paths, ensuring that they have the vital permissions to function thoroughly within managed airspace.
- Traffic Advisories: ATC additionally provides pilots with traffic advisories, alerting them to the presence of other planes of their location and presenting commands to keep secure separation.
- Emergency Assistance: In the event of an emergency, pilots depend upon ATC for assistance and steering, coordinating with controllers to navigate thoroughly to the nearest airport and facilitate emergency services.
Interaction with Airlines and Airports
Air Traffic Control doesn’t perform in isolation. It’s part of a broader aviation environment that includes airlines and airports, and collaboration among those entities is essential for making sure smooth and green operations.
- Slot Management: ATC works carefully with airways and airports to manipulate slot allocations, ensuring that there are enough assets to be had to accommodate scheduled flights and limit delays.
- Ground Operations: ATC coordinates floor movements with airport government and floor coping with offerings, ensuring that planes are able to taxi to and from the runway accurately and efficiently.
- Airport Capacity Management: ATC collaborates with airports to optimize runway usage and control congestion, assisting to maximize airport capability and minimize delays for arriving and departing flights.
Cooperation with Aviation Authorities
Behind the scenes, Air Traffic Control collaborates carefully with aviation authorities at the local, national, and global levels to ensure compliance with regulations and preserve the best requirements of safety and performance.
- Regulatory Compliance: ATC adheres to policies and directives issued by the aviation government, making sure that every one operations are conducted in accordance with established standards and techniques.
- Safety Oversight: Aviation authorities offer oversight and law of ATC operations, undertaking audits and inspections to ensure compliance with protection standards and discover areas for development.
- Training and Certification: Aviation authorities are chargeable for putting schooling necessities and certification standards for Air Traffic Controllers, ensuring that they own the necessary expertise and capabilities to perform their duties adequately and correctly.
Safety and Efficiency in Air Traffic Control

Risk Management Strategies
When it comes to Air Traffic Control, protection is the number one precedence. That’s why ATC employs a variety of danger management strategies to become aware of, check, and mitigate potential dangers before they boost into safety incidents.
- Proactive Monitoring: ATC continuously video display units air site visitors and weather situations to identify any capacity dangers or threats to safety.
- Safety Reviews: Regular protection reviews and audits are performed to become aware of trends, analyze safety facts, and put in force corrective actions to deal with any safety worries.
- Collaborative Decision Making: ATC collaborates with pilots, airlines, and other stakeholders to make informed selections and mitigate dangers in actual-time.
Emergency Response Protocols
Despite rigorous safety measures, emergencies can nonetheless occur within the world of aviation. That’s why Air Traffic Control has robust emergency reaction protocols in location to make certain fast and effective movement in times of crisis.
- Clear Communication: During emergencies, ATC maintains clean and concise conversation with pilots, imparting guidance and assistance as wanted.
- Coordination with Emergency Services: ATC coordinates intently with emergency services at the floor to facilitate a rapid reaction and make sure the safety of passengers and group.
- Contingency Planning: ATC develops contingency plans for various emergency scenarios, making sure that controllers are organized to respond quickly and efficiently to any situation.
Enhancing Efficiency through Technology
In addition to safety, Air Traffic Control is likewise targeted on improving efficiency to accommodate the growing call for air travel. Technology performs a key function in this effort, permitting ATC to optimize airspace utilization and streamline operations.
- Automation: Advanced automation tools help ATC manage air site visitors extra efficiently, lowering controller workload and minimizing the danger of human blunders.
- Data Sharing: ATC shares real-time statistics with airways, airports, and other stakeholders to improve situational awareness and optimize flight routes.
- NextGen Technologies: Next Generation Air Traffic Management systems leverage contemporary technologies along with satellite navigation, statistics communications, and artificial intelligence to beautify performance and potential within the airspace gadget.
Future Trends and Innovations

Next-Gen Air Traffic Management Systems
The future of Air Traffic Control is brighter than ever, thanks to the development of Next-Gen Air Traffic Management structures. These current technologies are revolutionizing the way air site visitors are controlled, paving the way for safer, more green, and environmentally sustainable aviation.
- Satellite Navigation: Next-Gen systems leverage satellite-primarily based navigation technologies, including GPS, to provide more particular and reliable positioning facts to pilots and controllers.
- Data Communications: Next-Gen structures allow virtual statistics communications among ATC and aircraft, replacing conventional voice communications and improving performance and accuracy.
- Performance-Based Navigation: Next-Gen introduces overall performance-based navigation approaches, allowing planes to fly more direct routes and decrease gas intake and emissions.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to play a giant position within the destiny of Air Traffic Control, presenting new opportunities to decorate safety, efficiency, and selection-making.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can examine full-size quantities of records to discover patterns, tendencies, and potential protection risks, helping ATC assume and mitigate troubles before they enhance.
- Automated Decision Support: AI-powered selection aid tools assist controllers in making quicker, extra knowledgeable decisions, enhancing situational attention and lowering workload.
- Machine Learning: By continuously gaining knowledge from actual-international information and comments, AI structures can adapt and evolve over the years, turning into extra powerful and efficient in managing air site visitors.
Sustainable Aviation Practices
As issues concerning climate exchange and environmental sustainability grow, the aviation industry is more and more specializing in adopting sustainable practices, and Air Traffic Control is not an exception.
- Green Flight Routes: Next-Gen systems enable the advent of extra gas-efficient flight routes, reducing fuel intake and emissions at the same time as preserving protection and efficiency.
- Alternative Fuels: ATC is exploring the usage of opportunity fuels, such as bio-fuels and hydrogen, to strengthen aircraft, reducing carbon emissions and environmental effect.
- Noise Abatement Procedures: ATC implements noise abatement tactics to limit the effect of aircraft noise on nearby communities, enhancing the nice of life for citizens near airports.
Conclusion

Recap of Key Points
As we wrap up our exploration of the basics of Air Traffic Control, allow us to take a second to recap the key points we have included along the way.
- Air Traffic Control is the invisible hand that courses the skies, making sure the safety and efficiency of air travel.
- From Ground Control dealing with aircraft moves at the floor to Tower Control overseeing runway operations and En-course Control guiding aircraft via the skies, each department of ATC performs a vital role in retaining our skies secure.
- Collaboration with pilots, airways, airports, and aviation authorities is critical for the success of Air Traffic Control, ensuring smooth and efficient operations and retaining regulatory compliance.
- Safety and performance are the twin pillars of Air Traffic Control, using innovation and technological advancements to beautify the future of aviation.
Importance of Continued Learning in Air Traffic Control
But our journey does not quit right here. In reality, it’s simply the beginning. The subject of Air Traffic Control is constantly evolving, with new technology, rules, and challenges rising all of the time. That’s why persevered studying is so essential for Air Traffic Controllers and aviation lovers alike.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of today’s tendencies in Air Traffic Control, from Next-Gen technology to sustainable aviation practices.
- Professional Development: Take advantage of education possibilities, seminars, and workshops to enhance your abilities and expertise in ATC.
- Adapt to Change: Embrace exchange and be open to new ideas and innovations within the subject of Air Traffic Control, as they can cause more secure, greater green operations.
Encouragement for Further Exploration
So, as we conclude our adventure through the fundamentals of Air Traffic Control, I inspire you to continue exploring this charming discipline and delving deeper into its intricacies. Whether you’re thinking about a profession in ATC, an aviation fanatic, or truly curious about how planes navigate the skies, there’s constantly extra to examine and discover.
- Dive Deeper: Explore advanced topics in Air Traffic Control, along with radar structures, verbal exchange devices, and emergency reaction protocols.
- Connect with Others: Join on-line forums, attend aviation activities, and hook up with fellow enthusiasts and specialists to percentage understanding and reviews.
- Inspire Others: Share your passion for Air Traffic Control with others and encourage the next era of aviation experts to pursue careers in this dynamic discipline.
FAQs

- What is Air Traffic Control (ATC)?
- Air Traffic Control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based controllers who manage the safe and orderly flow of aircraft in the sky and on the ground. They ensure that aircraft maintain safe distances from each other and follow designated flight paths, helping to prevent collisions and maintain overall aviation safety.
- How does Air Traffic Control communicate with pilots?
- Air Traffic Controllers primarily communicate with pilots using Very High Frequency (VHF) radios. Pilots and controllers exchange information verbally, including clearances for takeoff and landing, route instructions, and weather updates. In addition to voice communication, controllers may also use data link systems for text-based communication with aircraft.
- What are the main responsibilities of Air Traffic Controllers?
- Air Traffic Controllers have a range of responsibilities, including providing clearances for aircraft to take off and land, monitoring and managing the flow of air traffic, maintaining separation between aircraft, providing weather and traffic information to pilots, and coordinating with other ATC facilities.
- How do Air Traffic Controllers handle emergencies?
- In the event of an emergency, Air Traffic Controllers follow established protocols to ensure the safety of the aircraft and its occupants. They provide guidance and assistance to pilots, coordinate with emergency services on the ground, and facilitate the aircraft’s safe landing at the nearest suitable airport.
- What are some challenges faced by Air Traffic Controllers?
- Air Traffic Controllers face various challenges in their work, including managing high volumes of air traffic, coping with adverse weather conditions, handling emergency situations, and maintaining situational awareness in complex airspace environments. Additionally, factors such as fatigue and stress can impact controller performance, highlighting the importance of effective stress management and workload management strategies.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61556242913524
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/contentflyers0/
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/contentflyers0/
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/contentflyers0/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/user/contentflyers0
Medium: https://medium.com/@contentflyers0/
